Antimicrobial Resistance
Home ㅤ>ㅤ Antimicrobial Resistance

Challenge
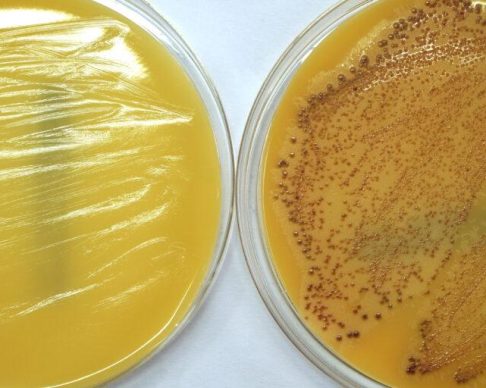
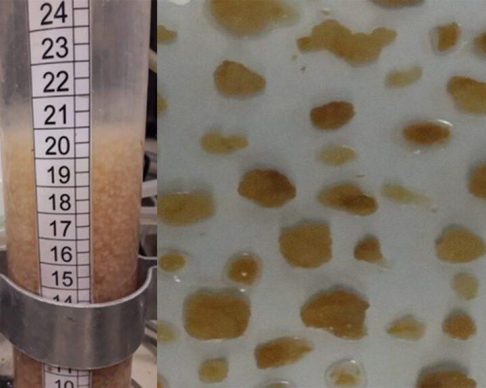
Appropriate antibiotic use has the power to save lives in the most vulnerable communities, and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) impacts multiple global health priority areas: HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, maternal and neonatal health, pneumonia, and enteric and diarrheal diseases. It is critical to better understand the prevalence of AMR and its impact on mortality in developing countries so that access to appropriate antibiotics is ensured while inappropriate use of antibiotics is limited. In particular, there is a need to better understand resistance in bacterial infections of newborns and young children – and to this end, understanding what is the prevalence of AMR in the community, how it impacts mortality, and how it impacts health targets. Tackling AMR will require a global, coordinated approach and the linking together of different research communities for new perspectives on the problem.

Goal
The program pursued new approaches with the potential to transform public health action on a regional or global scale by identifying and filling gaps in knowledge on the burden of resistance to antibacterial agents.
Specifically, the financed projects proposed innovation in the following areas:
- Data sources: Pilot tests of new sources of data, particularly those that would bring together different research communities from different disciplines for new perspectives on the problem;
- Analytical methods: Pilot tests of bioinformatics approaches, including new ways to analyze, combine or connect existing databases;
- Biomarkers: Pilot tests of new biomarkers or combinations of biomarkers that could lead to a new understanding of the actionable implications of antimicrobial resistance surveillance data;
- Low-cost technologies and products: Exploratory work in developing new technologies and products, including:
- those that specifically target improved infection prevention and control in healthcare settings to reduce reliance on healthcare provider behavior change, and
- technologies to remove antibiotics from effluents.

Project

Published Studies